A domain name is an address you type into your web browser to access a website.
Although a domain is the address used to access a website, it can often be confused with a URL which is the entire address including all of the colons, slashes AND domain name. A URL and a Domain Name are very similar but there is a distinct difference.
To answer what a domain name is I will first explain what a URL is.
What is a URL?
Uniform Resource Locator or URL for short refers to the entire address used to visit a website. A URL includes colons, slashes and the domain name.
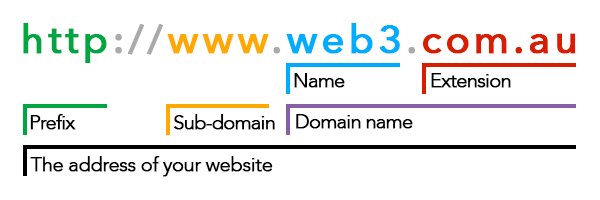
The URL for this page is ‘https://web3.com.au/what-is-a-domain-name/’. This address contains https:// which tells the browser that you are using a domain name.
This is followed by the domain name itself (www.web3.com.au or web3.com.au — both are valid but you should choose to use one or the other but not both). This points to the server where the website is hosted.
After the domain name is the extensions (/what-is-a-domain-name/) which is used to form the navigation hierarchy of the website.
So what is a Domain Name
A domain name is the part of the URL in between the http:// (or the secured version https://) and the following slashes and extensions.
A domain name usually spells one or many words but can contain any number of these characters:
- Letters (abc)
- Numbers (123)
- Dashes/hyphens (—)
Spaces are not allowed and the domain can’t begin or end with a dash. Multiple dashes right next to each other can be used but I recommend against this for readability sake.
After the characters follows an extension. The extension used is most commonly what is called a TLD or a top level domain such as .com, .net, .info, .biz and so on.
The .com TLD is by far the most common extension and was the first domain type to be used. As well as TLD’s there are Second level domains or 2LDs. 2LDs are domain names containing another level after the first suffix. For example; .com.au is a second level domain that contains an additional suffix after the .com.
The .au signifies that the website originates from Australia.
Domains and Email Addresses
Emails also rely on domain names to work. To use your own custom branded email address, you need to own that domain.
Using your own custom branded email addresses has many advantages for branding and professional communications. It is possible to register your own domain name simply to have your own custom branded email address instead of relying on generic services such as Hotmail or Gmail.
If you are interested in a custom branded email account then we can help you get started.
Register your Custom Domain Name
Would you like to have the benefits of using your own custom domain name? Make sure your domain is short and concise whilst helping to define your brand.
You can read more about choosing the best domain name for your business here or if you need a hand registering your domain name or setting up a custom branded email account then we can help with that.


